Tamagotchi 商店
在本课程中,你将学习智能合约中的购买过程。我们将涵盖以下概念:
- 如何编写智能合约以定义商店合约状态的结构。
- 创建新属性以及如何将它们出售给 Tamagotchi 合约。
- 从 Tamagotchi 合约接收消息。
- 使用异步的 main 函数。
- 在商店合约中创建新属性。
让我们开始吧。
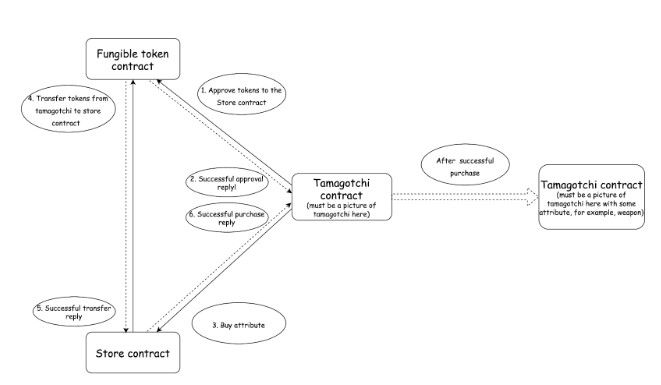
智能合约的购买过程包括三个简单的步骤:
第 1 步:从 Tamagotchi 获得批准 - Tamagotchi 向同质化代币合约发送消息,以批准将代币转移到商店合约。
第 2 步:选择属性 - 在获得批准后,Tamagotchi 向商店合约发送消息,指示它想要购买的特定属性。
第 3 步:完成交易 - 在接收消息后,商店合约采取行动。它向同质化代币合约发送消息,请求将代币转移到自身。如果转移成功,商店合约将选定的属性添加到 Tamagotchi 的属性列表中。
Coding
让我们开始编写智能合约。首先,我们将定义商店合约状态的结构:
pub struct AttributeStore {
admin: ActorId,
ft_contract_id: ActorId,
attributes: BTreeMap<AttributeId, (Metadata, Price)>,
owners: BTreeMap<TamagotchiId, BTreeSet<AttributeId>>
}
我们将使用类型别名来提高代码的可读性:
pub type AttributeId = u32;
pub type Price = u128;
pub type TamagotchiId = ActorId;
属性的 Metadata 包含以下字段:
pub struct Metadata {
/// The attribute title, for example: "Weapon".
pub title: String,
/// Description of the attribute.
pub description: String,
/// URL to associated media (here it should be an attribute picture).
pub media: String,
}
让我们定义商店合约必须执行的操作:
- 创建新属性并将其出售给 Tamagotchi 合约。
- 从 Tamagotchi 合约接收消息。
在实现这些功能之前,我们将为合约存储定义 store-io 包。这个包将帮助我们处理商店的输入和输出。
然后,我们将为合约编写 lib.rs 文件。
#![no_std]
use gstd::{prelude::*, ActorId};
pub type AttributeId = u32;
pub type Price = u128;
pub type TamagotchiId = ActorId;
#[derive(Encode, Decode)]
pub struct Metadata {
/// The attribute title, for example: "Weapon".
pub title: String,
/// Description of the attribute.
pub description: String,
/// URL to associated media (here it should be an attribute picture).
pub media: String,
}
#[derive(Encode, Decode)]
pub enum StoreAction {
CreateAttribute {
attribute_id: AttributeId,
metadata: Metadata,
price: Price
},
BuyAttribute {
attribute_id: AttributeId,
}
}
#[derive(Encode, Decode)]
pub enum StoreEvent {
AttributeCreated {
attribute_id: AttributeId,
},
AttributeSold {
success: bool,
},
}
商店合约将接受两种类型的消息: CreateAttribute 和 BuyAttribute。
在消息执行成功时,它将回复 AttributeCreated 或 AttributeSold。
现在,我们将编写合约的基本结构如下:
#![no_std]
use gstd::{msg, prelude::*, ActorId};
use store_io::*;
static mut STORE: Option<AttributeStore> = None;
pub struct AttributeStore {
admin: ActorId,
ft_contract_id: ActorId,
attributes: BTreeMap<AttributeId, (Metadata, Price)>
owners: BTreeMap<TamagotchiId, BTreeSet<AttributeId>>
}
impl AttributeStore {
fn create_attribute(&mut self, attribute_id: AttributeId, metadata: &Metadata, price: Price) {}
async fn buy_attribute(&mut self, attribute_id: AttributeId) {}
}
#[gstd::async_main]
async fn main() {
let action: StoreAction = msg::load()
.expect("Unable to decode `StoreAction`");
let store: &mut AttributeStore = unsafe {
STORE.get_or_insert(Default::default())
};
match action {
StoreAction::CreateAttribute {
attribute_id,
metadata,
price
} => store.create_attribute(attribute_id, &metadata, price),
StoreAction::BuyAttribute { attribute_id } =>
store.buy_attribute(attribute_id).await,
}
}
#[no_mangle]
extern "C" fn init() {
let ft_contract_id: ActorId = msg::load()
.expect("Unable to decode `ActorId`");
let store = AttributeStore {
admin: msg::source(),
ft_contract_id,
..Default::default()
};
unsafe { STORE = Some(store) };
}
我们使用 async fn main() 语法以及 #[gstd::async_main] 宏来替代 handle() 函数。当我们的合约中有异步函数时,异步的 main 函数成为程序的起始点。
buy_attribute 函数是异步的,因为商店合约需要发送消息给代币合约并等待回复。
现在,让我们实现 create_attribute 函数。
这个函数很简单,执行以下步骤:
- 验证发送消息的账户是否是合约管理员。
- 确保指定��的属性 ID 不存在。
- 创建一个新属性。
- 发送回复,指示属性的创建成功。
fn create_attribute(
&mut self,
attribute_id: AttributeId,
metadata: &Metadata,
price: Price
) {
assert_eq!(msg::source(), self.admin,
"Only admin can add attributes");
if self
.attributes
.insert(attribute_id, (metadata.clone(), price))
.is_some()
{
panic!("Attribute with that ID already exists");
}
msg::reply(StoreEvent::AttributeCreated { attribute_id }, 0)
.expect("Error in sending a reply StoreEvent::AttributeCreated");
}
接下来,让我们看看如何实现 buy_attribute 函数。
如前所述,该函数的作用是启动从 Tamagotchi 合约到商店合约的代币转移。
此外,它需要跟踪代币合约中的交易 ID。为了实现这一点,我们将在商店合约的状态中引入一个名为 transaction_id 的新字段。
商店合约负责跟踪同质化代币中的交易,并考虑其中的当前交易的 ID。
让我们为合约状态添加一个名为 transaction_id 的字段:
pub struct AttributeStore {
// ...
transaction_id: TransactionId,
}
该字段存储当前交易的 ID,并有助于跟踪代币转移的状态。对于 buy_attribute 函数来说,它允许我们启动转移、监视交易 ID,并等待来自同质化代币合约的成功转移的确认。
为了简化这个过程,我们将在合约存储的 store-io 中声明交易 id 的类型:
pub type TransactionId = u64;
接下来,让我们考虑以下情况:
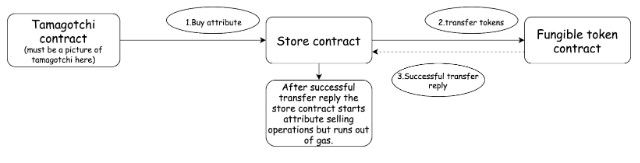
- Tamagotchi 向商店合约发送消息以购买属性。
- 商店合约发送消息给同质化代币合约,并收到关于成功代币转移的回复。
- 商店合约开始更改其状态。它将指定的属性添加到 Tamagotchi 所有权,但是耗尽了 Gas。
在上述描述的情景中,代币已经转移到了商店合约,但 Tamagotchi 没有收到它的属性。
为了防止这种情况发生,商店合约必须检测何时交易未完成,并根据情况继续执行。
让我们向 AttributeStore 结构中添加另一个字段:
pub struct AttributeStore {
// ...
transaction_id: TransactionId,
transactions: BTreeMap<TamagotchiId, (TransactionId, AttributeId)>,
}
当 Tamagotchi 发送购买消息给商店合约时,合约会检查 Tamagotchi 是否当前参与任何未完成的交易。如果存在未完成的交易,合约将检索与交易关联的交易号和属性 ID,并恢复它。
如果上一条消息没有完成,Tamagotchi 必须发送另一条相同的消息来完成交易。但是,Tamagotchi 可能会发送多个购买消息,而没有意识到某些消息未被交付。
为了处理这种情况,商店合约检查当前消息中指定的属性 ID,并将其与存储在交易中的属性 ID 进行比较。
如果前一条消息未完成,商店合约会告诉 Tamagotchi 完成前一个交易。否则,它将继续未完成的交易。
如果 Tamagotchi 没有未完成的交易,商店合约将增加 transaction_id 的值,并保存交易。
async fn buy_attribute(&mut self, attribute_id: AttributeId) {
let (transaction_id, attribute_id) = if let Some((transaction_id, prev_attribute_id)) =
self.transactions.get(&msg::source())
{
// If `prev_attribute_id` is not equal to `attribute_id`, it means the transaction wasn't completed
// We'll ask the Tamagotchi contract to complete the previous transaction
if attribute_id != *prev_attribute_id {
msg::reply(
StoreEvent::CompletePrevTx {
attribute_id: *prev_attribute_id,
},
0,
)
.expect("Error in sending a reply `StoreEvent::CompletePrevTx`");
return;
}
(*transaction_id, *prev_attribute_id)
} else {
let current_transaction_id = self.transaction_id;
self.transaction_id = self.transaction_id.wrapping_add(1);
self.transactions
.insert(msg::source(), (current_transaction_id, attribute_id));
(current_transaction_id, attribute_id)
};
let result = self.sell_attribute(transaction_id, attribute_id).await;
self.transactions.remove(&msg::source());
msg::reply(StoreEvent::AttributeSold { success: result }, 0)
.expect("Error in sending a reply `StoreEvent::AttributeSold`");
}
为了确保准确地跟踪事件,将 CompletePrevTx 事件包含在 StoreEvent 函数中。
好的,现在让我们创建一个函数来出售属性。
出售属性类似于执行 NFT 转移。在这种情况下,我们将属性 ID 分配给 Tamagotchi 合约。
首先,我们将为代币转移编写函数:
async fn transfer_tokens(
transaction_id: TransactionId,
token_address: &ActorId,
from: &ActorId,
to: &ActorId,
amount_tokens: u128,
) -> Result<(), ()> {
let reply = msg::send_for_reply_as::<_, FTokenEvent>(
*token_address,
FTokenAction::Message {
transaction_id,
payload: LogicAction::Transfer {
sender: *from,
recipient: *to,
amount: amount_tokens,
},
},
0,
0,
)
.expect("Error in sending a message `FTokenAction::Message`")
.await;
match reply {
Ok(FTokenEvent::Ok) => Ok(()),
_ => Err(()),
}
}
我们已经向代币合约发送了一条消息,并处理了其回复。合约通过检查是否收到 FTokenEvent::Ok 响应来确定消息处理的成功。
现在,我们准备编写出售属性的函数:
async fn sell_attribute(
&mut self,
transaction_id: TransactionId,
attribute_id: AttributeId,
) -> bool {
let (_, price) = self
.attributes
.get(&attribute_id)
.expect("Can't get attribute_id");
if transfer_tokens(
transaction_id,
&self.ft_contract_id,
&msg::source(),
&exec::program_id(),
*price,
)
.await
.is_ok()
{
self.owners
.entry(msg::source())
.and_modify(|attributes| {
attributes.insert(attribute_id);
})
.or_insert_with(|| [attribute_id].into());
return true;
}
false
}
首先,合约接收属性的价格。然后它调用 transfer_tokens 函数。如果代币转移的结果成功,属性将添加到 Tamagotchi 合约。
太棒了!我们已经完成了合约逻辑的编写。
现在,你的 Tamagotchi 可以具备购买属性的能力。
收获
- 与同质化代币合约通信。
- 如何处理不完整或不完美的交易。